New catalytic system for cross-coupling reactions
Référence
00755-05
Mots-clés
Statut des brevets
Provisional patent application US60996830 filed on December 5, 2007 and entitled « Arylations dans des conditions douces de nucléophiles azotés, oxygénés et carbonés par catalyse au Fer. »


Inventeurs
Marc TAILLEFER
Ning XIA
Florian MONNIER
Anis TLILI
Statut commercial
Exclusive or non-exclusive licence.
R&D Partnership
Laboratoire
Institut Charles Gerhardt – Institut de chimie moléculaire et des Matériaux, in Montpellier, France.
Description
CONTEXT
The diaryl ether structure is found in numerous important organic compounds in the pharmaceutical and polymer industries. The common synthesis of diaryl ethers usually requires the reaction of phenols with aryl halides in the presence of a catalyst containing a transition metal. It has been reported that Pd catalyzed methods can function in this role but their high costs and elaborate ligands are drawbacks when compared with copper mediated reactions. Indeed, in recent years much work has contributed to improving the traditional Ullmann ether synthesis which requires stoichiometric quantities of copper and harsh conditions. In spite of great advances in the use of copper catalysts associated with specific ligands, the aryl chlorides are still problematic substrates. Thus a convenient and general method for arylation from aryl chlorides should be of great interest to industrial production and laboratory research due to their low cost and ready availability.
We now report the first general method for copper catalyzed arylation of phenols from aryl chlorides. An additional finding of this study is the iron catalyzed arylation of phenols from aryl iodides.
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
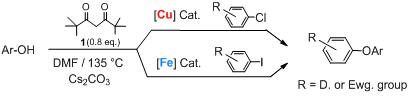
The first general entry into copper catalyzed arylation of phenols from aryl chlorides is the principal outcome of the study presented in this article. The use of the 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-3,5-heptanedione 1 as ligand is the key to the success of this reaction. An additional finding of this study is the (iron/1) catalyzed arylation of phenols from aryl iodides.
BENEFITS
We have checked the utility of diketone 1 in copper catalyzed arylation of phenols from aryl chlorides. This reaction -of considerable economic importance- provides a challenge to which we supply the first satisfying solution. Commercial availability, low cost and low toxicity of the copper system makes it very competitive to existing Pd-based protocols. Moreover, our method is easily adaptable to an industrial scale for which financial and environmental factors are of greater importance. Finally, we have also shown the efficiency of catalysts employing diketone 1 using iron alone as the metal and its use with both metals to afford a clean entry into the regioselective synthesis of unsymmetrical aromatic polyethers.
PUBLICATIONS
Copper- or Iron-catalyzed Arylation of Phenols from respectively aryl chlorides and aryl iodides.
N. Xia, M. Taillefer.
Chemistry, a European Journal, 2008, 14, 6037
For further information, please contact us (Ref 00755-05)